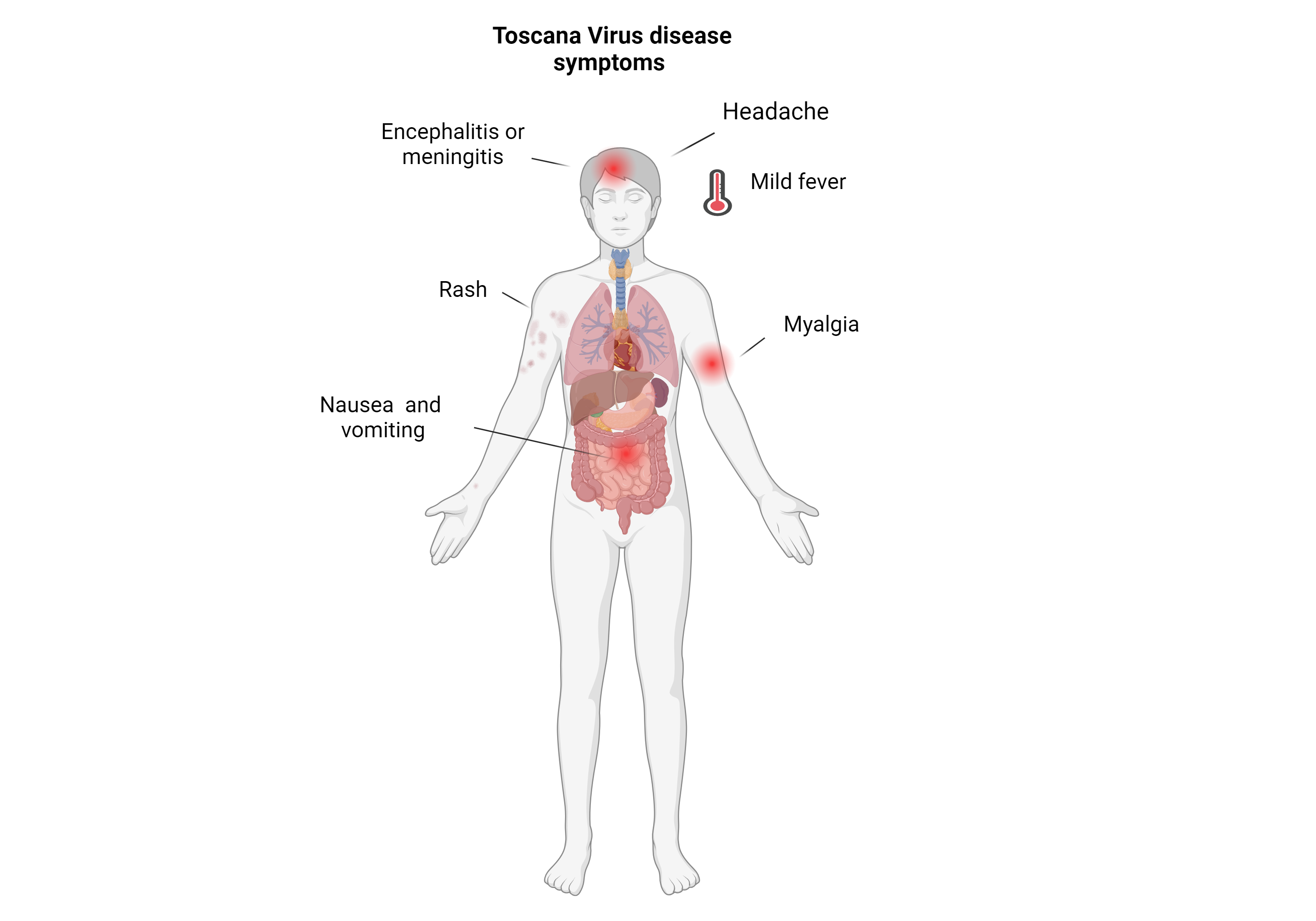
Most people infected are asymptomatic .
In serious cases that go undiagnosed, acute meningitis, meningoencephalitis and encephalitis may occur. In rare instance, fatal encephalitis has been reported.
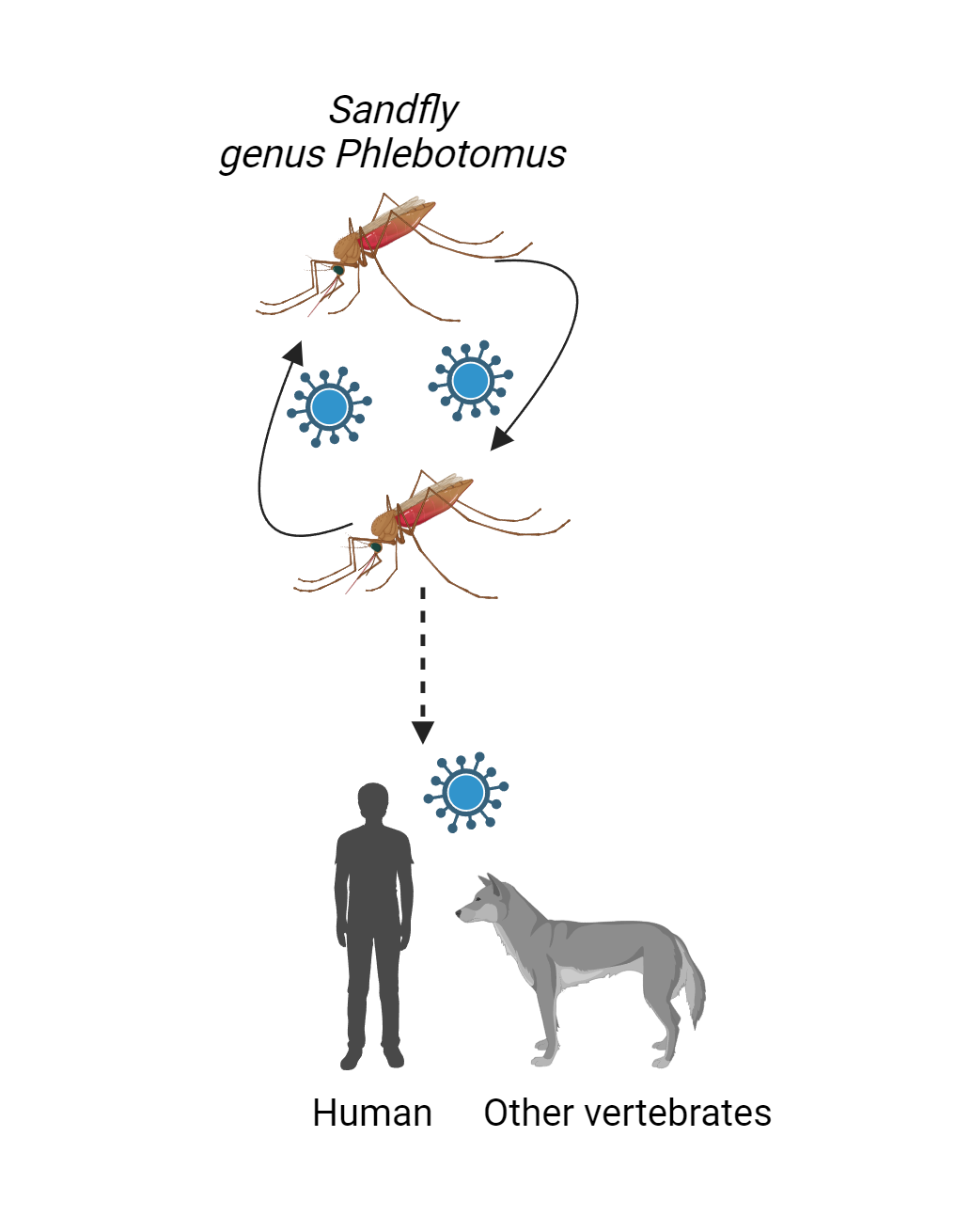
Toscana virus was first isolated in 1971 from sand flies collected in the Tuscany region of Italy and first evidence for its propensity to cause human disease was reported in 1983.
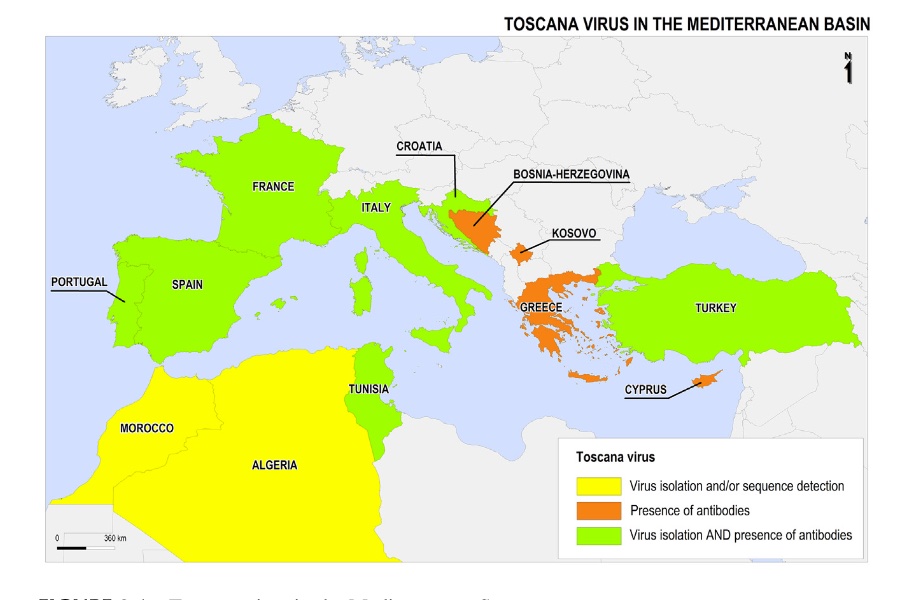
This virus is a leading cause of acute meningitis between May and October in Central Italy and in other northern Mediterranean countries (Croatia, France, Greece, Portugal and Spain) as well as several of the eastern Mediterranean countries (Cyprus and Turkey).
It is among the 3 most prevalent viruses associated with meningitis during the warm seasons: the other two are enteroviruses and herpesviruses.
The toolbox for this virus is currently in development. Please contact us via info@virusbankplatform.be for more information.